
In this article, we are studying the fundamentals of Electric Fuse. It is switchgear protection equipment that we use daily even at our house.
Fuse is a protector and safety device for power circuits. It helps to protect from fault conditions such as short circuits, overload, damaged equipment, or mismatched load conditions.
We will see in detail.
What is an Electric Fuse?
The basic definition-
A small piece of wire or thin metallic strips of electrical equipment that protect the electrical circuit or system from the excessive flowing current is called Electric Fuse.
In 1890, the first electric fuse is invented by Thomas Alva Edison.
An electrical fuse works based on thermal properties such as the temperature heating effect which is generated by the electrical energy.
A fuse consists of two conducting elements such as short wire and thin metallic strips. These elements are made by a metal conductors like copper, silver, aluminum, and zinc.
Generally, a low melting point and high conductivity material are mostly used in the fuse.
It plays both protector and safety device roles for the protection of the power system. It helps to clear the automatic fault and to avoid damage to electric devices.
Electric Fuse Symbol:
By IES, IEEE/ ANSI standard, the fuse has represented by different symbols.
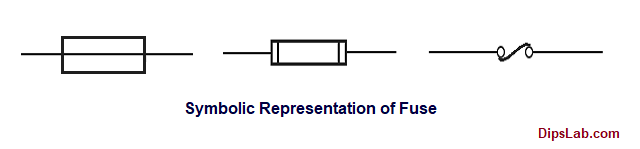
Why is fuse mostly used in an electrical circuit?
- Fuse performs detection and interruption functions in fault conditions.
- It works as an automatic protector i.e. it can easily stop the power flowing through the fault system.
What are the types of fuse?
An electric fuse is classified based on the current and voltage rating, carrying capacity, and overcurrent breaking capacity.
Based on the different types of current, there are two types of fuse.
- DC Fuse
- AC Fuse
Again, the AC fuse is classified into two different parts-
- High Voltage (HV) Fuse
- Low Voltage (LV) Fuse
Do you want to know more fuse types? Check this electrical fuse classification diagram.
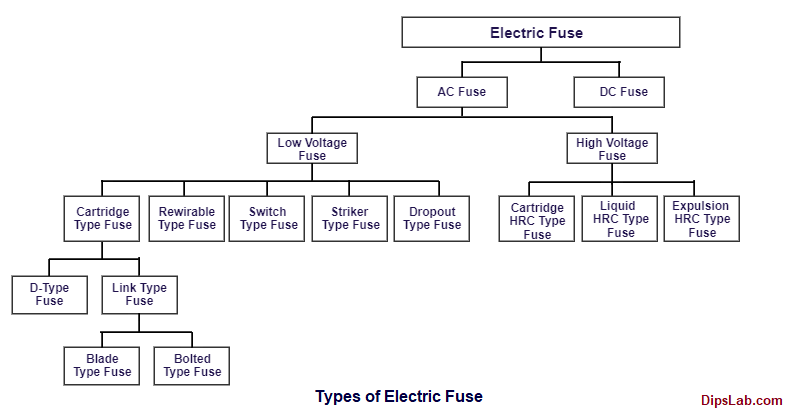
The high voltage type fuse is used in the circuit having a voltage range up to 66 kV. The low voltage type fuse is used in the circuit having a range up to 400V.
These different types of fuses are designed with a specific perspective, current, and voltage rating capacity.
You can get these types of fuse easily in a market. They don’t have much cost.
How does Electrical Fuse Work?
What is the working of Electrical Fuse?
An electrical fuse works based on the heating effect which is produced by electrical energy.
How is the electric fuse connected in the circuit?
In the electrical circuit, the fuse is generally connected in series. (You can read the difference between series and parallel circuits.)
At the normal condition, the fuse carries the current at normal temperature without overheating effect.
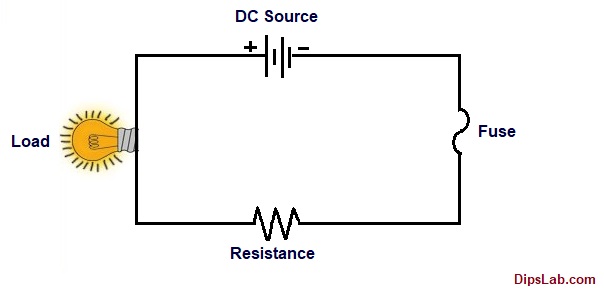
Electric Circuit with connected Fuse
In a short circuit or overload condition, when excessive current flows through an electric circuit (beyond its rated current carrying capacity), a high temperature will generate.
Due to raising the temperature, the fuse element will melt and disconnect the power circuit.
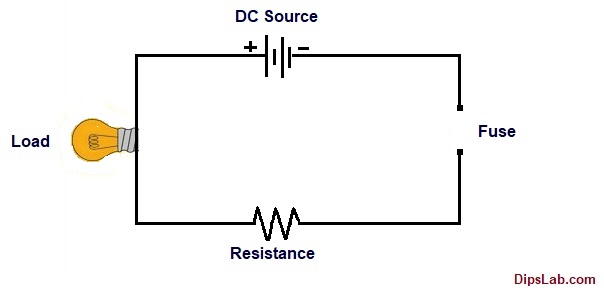
Electric Circuit with disconnected Fuse
Hence, the fuse helps to provide protection for the circuit and other connected devices.
What is Fusing Current?
The minimum current at which fuse element melts, disconnects and protects the device from fault is called as ‘Fusing Current’.
It depends upon various factors like- fuse elements (wire or strip) material, dimensions, types, and other things.
The fusing current factor is the ratio of minimum fusing current to the rated carrying current.
Fusing Current Factor = (Minimum Fusing Current / Rated Carrying Current)
Use of Electrical Fuse | Applications
What is the usage of fuse?
- In the home wiring, we use an electric fuse. Mostly, a semi-enclosed rewirable fuse or KitKat fuse is used.
- Also, it is used as a protector device in domestic appliances like refrigerators, Air conditioning (AC), washing machine, and many more home appliances.
- It is useful for the protection of the lightning and heating effect system.
- Fuse provides the protection system for industrial equipment such as electric motor/generator protection, transformer, capacitor, etc.
Overall, it is used for overload or short circuit protection in the power system.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Electric Fuse
There are many protection devices in the market. I am explaining the multiple advantages and disadvantages of Electric fuse over other circuits breakers.
Advantages of Electric Fuse:
- The basic advantage of the fuse is that it is used as a safety and protector device to protect the electrical devices when the current exceeds the current limit.
- It helps to perform both operations like detection and interruption in a fault condition.
- You can find the different types of fuses easily in the market. They don’t have much cost.
- It occurs in a small size, you can easily transport or handle as compared to other switchgear protection equipment.
- It requires no more maintenance.
- Without noise, flame, gas, or smoke, it can automatically break the power circuit in a fault condition.
- It requires a minimum time (milli-sec i.e. 0.002 sec) to break the circuit in a fault condition.
- At-fault conditions, the fuse gives less time to detect and interrupt the electric circuit than the circuit breaker (CB).
Disadvantages of Electric Fuse:
- After every fault condition, we require to replace the electric fuse. Or you can also rewire the fuse.
- Fuse is not recommended to use in high voltage rating circuits.
- It can not be used multiple times after the fault conditions.
This is all detail about the Electric Fuse. If you have any queries about the electric fuse, you can freely comment in the given comment section.
Related Read:
- Electrical Fuse Vs Circuit Breaker
- Electrical Vs Electronics Circuit
- MCB Vs MCCB Circuit Breaker
- Electrical Transformer
- Electrical Vs Magnetic Circuit
- Electrical Measuring Instruments
- Electrical & Electronics Project Based on Fuse
Thanks for Reading!
This post cleared all my doubt related to this topic.
Good 🙂
Great am happy with the information….
Thanks, Donald 🙂