In an earlier article, we have studied the corona effect in the power system. Here, I will explain the skin effect with basic terms like definition, diagram, affecting factors, formula, etc.
Let’s dive from the basic.
Table of Contents
What is skin effect in electrical?
The accumulation of current on the surface of the conductor and the tendency of the flow of the current on the surface of the conductor is referred to as a ‘Skin-effect‘.
This effect is mainly due to the magnetic flux linkage of the center conductor is more compared to the outermost conductor.
Due to that the impedance or inductance of the central strand of the conductor is more which results in the deviation of the current through the outer strand of the conductor.
So, the non-uniformity of these uneven flux linkages would be the cause of this effect.
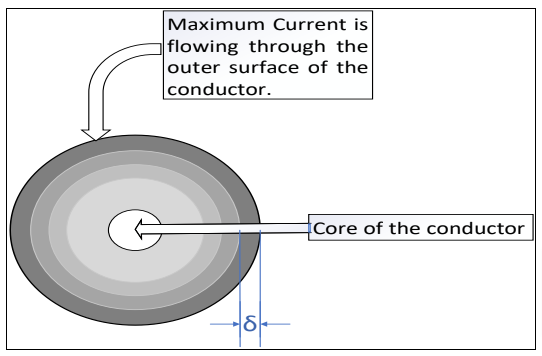
Geometry of Conductor
How to calculate Skin Effect?
Here, in the above diagram dark portion indicates the current density which is more at the outer surface of the conductor. And it goes decreasing when we move towards the core of the conductor.
Due to this imbalance of the magnetic flux linkage then the effective area of the current-carrying path decreases and which creates the difference between the AC and DC resistance.
As in DC system this effect is not present. This AC resistance can be approximated by-
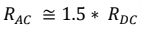
Skin effect basically depends on skin depth.
What is a skin depth?
The definition of skin depth is the distance from the outer surface to the strand of the conductor where the flow of current is maximum. This is indicated as ‘ δ ’ in the above figure.
Skin depth (δ) is calculated by using the formula as below,
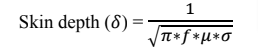
Where,
f- Frequency of the system
μ- Relative permeability of conductor
σ- Conductivity of conductor
Skin depth is low which indicates the skin effect is more or vice versa.
This effect is more in communication lines compared to the power line as the frequency of the communication line is in MHz.
This effect is low for the hollow conductors, so they are preferred for the large current rating of the load.
This is the explanation of the skin effect in power transmission lines. In an upcoming tutorial, I will explain the proximity effect.
Read more related tutorial:
- Surge Impedance Loading & Ferranti Effect
- Alternating current vs Direct current
- Electrical circuit vs Magnetic circuit
- Single-phase vs Three-phase AC systems
- Overhead line vs Underground cable
- Transmission line vs Distribution line
- On-Grid system vs Off-Grid system
- Star Connection vs Delta Connection of AC Systems