
Ever want to learn Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) programming? especially, ladder diagram programming.
Along with basic digital electronic logic gates concept, programming rules and you have to learn programming instructions.
In the earlier tutorial, I have already explained the different types of logic gates and programming rules for writing PLC programming.
If you have not gone through it, you can check here.
Now in this article, I am listing the topmost useful PLC programming instructions. These instructions are useful for ladder diagram programming language.
[Explained with Ladder Diagram(LD)]
Let’s dive in from the basics.
Table of Contents
What is the Instruction?
Instruction is nothing but the command that we give to the machine to perform certain tasks.
We can club multiple instructions to perform one logical operation. The sets of multiple operations are called as ‘Program‘.
In PLC, the different instructions are used to control and maintain the operations. Every instruction is having different specifications like – working principle, function, use, advantage, etc.
According to the PLC program or project requirement, different instructions are needed.
According to different PLC software brands, there are different instructions sets.
Every instruction has input and output.
Input/Output Basics:
In PLC programming, inputs and outputs are very basic terms.
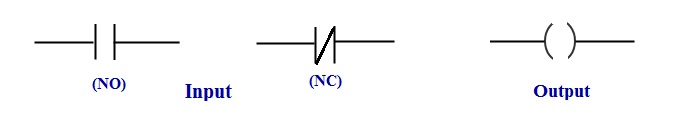
- Input is shown by two parallel lines- Normally Open (NO) or Normally Closed (NC)
- Output is shown by Parentheses or round brackets.
This is easily understood by the below diagrams.
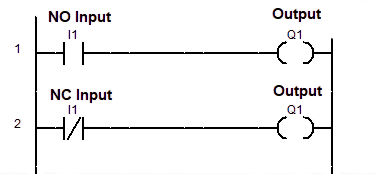
As shown in given LD program, NO & NC input are connected with the output.
PLC Programming Instructions Types and Classifications
What are different instructions of PLC?
Let’s see here, the different types of instructions set which are used for the ladder diagram PLC programming.
1. Basic PLC Programming Instructions
- Input (I or X) Instruction
- Output (O or Q ) Instruction
- Set (S) and Reset (R) Instruction
- Latch (L) and Unlatch (U) Instruction
The Set/Reset and Latch/Unlatch instructions are similar to each other.
The only difference is- Latch/Unlatch instructions are used for the cyclic process. I have already explained in the PLC programming rules tutorial.
2. Time-Based PLC Programming Instructions
The timer instructions follow task or command for/at a particular duration of time.
Sometimes, timers are used for the ON/OFF condition for the PLC.
Here are different timer instructions that fall into this category.
- Single Pulse (Monoflop) Timer Instruction
- Flashing Timer Instruction
- On Delay Timer (TON) Instruction
- Off Delay Timer (TOFF) Instruction
- Retentive Timer (RTO) Instruction
- Pulse Timer (S-Pulse) Instruction
- Pulse Extended Timer (S-PEXT) Instruction
- On Delay Timer (S-ODT) Instruction
- Off Delay Timer (S-OFFDT) Instruction
- Extended On Delay Timer (S-ODTS) Instruction
- On Delay with Random Time Timer Instruction
In an earlier tutorial, I have already explained the types of timer instructions with an example.
Which PLC brands use which Timer Instructions?
- On Delay timer, Single Pulse (Monoflop) timer, On Delay with Random Time timer and Flashing timer are used in the ABB PLC.
- On Delay timer (TON), Off Delay timer (TOFF) and Retentive timer (RTO) are used in the AB PLC.
- Pulse timer (S-Pulse), Pulse Extended timer (S-PEXT), On Delay timer (S-ODT), Extended On Delay timer (S-ODTS) and Off Delay timer (S-OFFDT) in the Siemens PLC.
2. Counting-Based PLC Programming Instruction
Counter instructions are used for counting pulse in the PLC program. You can count the pulse or digit by increasing or decreasing.
The classification of different Counter instructions are-
- Up Counter (CTU) Instruction
- Down Counter (CTD) Instruction
- Up-Down Counter Instruction
These three different counters are widely used in AB PLC and Siemens PLC programming.
3. Comparison Based PLC Programming Instruction
These instructions are used to compare inputs.
Here are some of the basic instructions used for comparison.
- Greater than (GET) Instruction
- Lesser than (LET) Instruction
- Equal to (EQU) Instruction
- Not Equal to (NEQ) Instruction
- Greater than or equal to (GEQ) Instruction
- Lesser than or equal to (LEQ) Instruction
- Increment and Decrement Instruction
- Limit (LIM) Instruction
Most of the instructions are self-explanatory. And you can easily understand their purpose.
4. Mathematical PLC Programming Instruction
These PLC instructions are used to perform different mathematical operations like arithmetic, trigonometric and logarithmic operations.
- Addition (ADD) Instruction
- Subtraction (SUB) Instruction
- Multiplication (MUL) Instruction
- Division (DIV) Instruction
- Square Root (SQRT) Instruction
- Absolute (ABS) Instruction
- Sine (SIN) Instruction
- Cosine (COS) Instruction
- Tangent (TAN) Instruction
- Arc Sine (ASN) Instruction
- Arc Cosine (ACS) Instruction
- Arc Tangent (ATN) Instruction
- Natural Log (LN) Instruction
- Log to Base 10 (LOG) Instruction
Note: These mathematical instructions, comparative instructions, and counter instructions are used for the counting pulse as per project requirement.
5. Data Transfer Based PLC Programming Instruction
On the basis of programming data transfer, multiple instructions are applicable for multiple purposes.
Here, I am shortlisting the topmost instruction used for data transfer.
- Fill File (FLL) Instruction
- Move (MOV) Instruction
- Copy (COP) Instruction
- Jump (JMP) Instruction
- Jump Not (JMPN) Instruction
- Conditional Jump Instruction
- Jump to Subroutine (JSR) Instruction
- Subroutine (SBR) Instruction
- Return (RST) Instruction
- Suspend (SUS) Instruction
- Lable (LBL) Instruction
- Jump and Lable (JMP & LBL) Instruction
- Master Control Set (MCS) instruction
- Master Control Reset (MCR) instruction
- One-Shot Rising (OSR) Instruction
- One-Shot Falling (OSF) Instruction
- Convert from Integer to BCD (TOD) Instruction
- Convert from BCD to Integer (FRD) Instruction
- Temporary End (TND) Instruction
- Convert Radians to Degrees (DEG) Instruction
- Convert Degrees to Radians (RAD) Instruction
7. Logical or Bitwise PLC Programming Instruction
Many times, we need to perform logical operations on input data. The logical instruction basically depends on the logic gate concept.
- Bitwise NOT (NOT) Instruction
- Bitwise AND (AND) Instruction
- Bitwise OR (OR) Instruction
- Bitwise Exclusive OR (XOR) Instruction
- Flip-Flop (RS or SR Flip-Flop) Instruction
- Positive H Trigger (P) Instruction
- Negative H Trigger (N) Instruction
To understand the logical operations, check logic gates using PLC programming.
8. Sequence-Based PLC Programming Instruction
To implement certain logic, we need to follow a particular sequencing. Here are some of the sequencing operations you can perform using PLC instructions.
- Sequencer Input (SQI)
- Sequencer Output (SQO)
- Bit Shift Left (BSL)
- Bit Shift Right (BSR)
- Sequencer load (SQL)
- Sequencer compare (SQC)
What’s Next?
I have listed the most common, important and widely used instructions for the ladder diagram PLC programming.
For the industrial environment, AB PLC and Siemens PLC software are used. One of the advantages of using these PLC softwares is that they have a lot of instructions set. This makes your job of writing PLC programming logic easy.
I have listed different PLC instructions. If you want to know detail about any instruction, let me know in the comment.
Ready for PLC Test:
If you are ready for online test, click on is a PLC Automation Quiz.
Happy PLC Learning!
If you give instructions command with an example that would be great.
Okay, Ranjit. I have already explained the timer instructions detail with an example.
Soon, I will share each type of instruction one by one.
Sequencer Input (SQI)
Sequencer Output (SQO)
Bit Shift Left (BSL)
Bit Shift Right (BSR)
Sequencer load (SQL)
Sequencer compare (SQC)
Can you give me example of these please. with program.
Thanks, Prasad for the suggestions. I will try to cover all these instructions with an example.
Really appreciating work. Thanks for sharing ma’am. It’s really helpful.
Thanks, you too Pranay 🙂
Thanks.
Nicely curated article. I really appreciated your work.
Thank you very much 🙂
Hi ma’am
Hi,
Kindly let me know how I may assist you.
Thanks a lot for the tutorial.
Glad 🙂
It is very useful. Thank you for sharing.
Thanks, you too:)
Good crisp introduction to instruction.
Thank you very much 🙂
Much thanks for the tutorial!
Glad to enjoyed it.