When you study electrical devices or components, you should know the basic information about common electrical components.
One of the common components in electrical is Resistors. And its value is calculated in Resistance.
In this article, I explain- ‘What is the Resistance?’, the formula and the use of resistors in electric circuits.
Table of Contents
What is Resistance?
Definition of Resistance:
The property of the substances which opposes to the flowing of current or limiting current in an electric circuit is known as ‘Resistance’.
Symbolic Representation of Resistance:
In an electrical and electronic circuit, the resistance is shown by the given symbol. Here, Resistance is signified by the ‘R’.
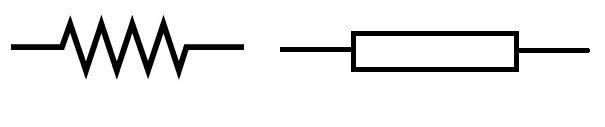
Resistance (R)
The schematic diagram of an electrical circuit that consists of resistance (R) with a connected voltage source.
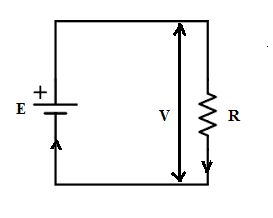
Electrical Circuit with Resistance
For Example, if the one amp current passes through the circuit which having a voltage of one volt, the resistance is calculated as one ohm.
Resistance, (R)= [(Voltage)/(Current)]= [(1 volt)/(1 Ampere)]= (1 ohm)
We can conclude that, the resistance is always inversely proportional to electric current. So, high resistance provides a low current in the circuit and vice-versa.
And insulators usually have more resistance and good conductors have low resistance.
Measuring Instrument to Identify Resistance
The resistance is measured in an Ohmmeter or Digital Multimeter.
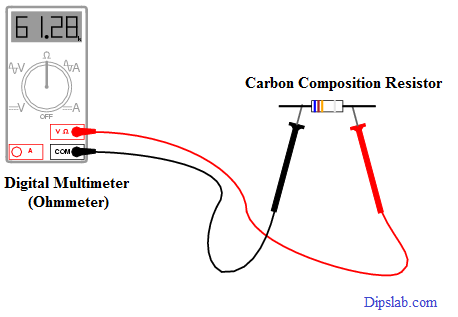
Unit: It SI unit and CGS Unit are Ohm (represented by ‘Ω‘).
How to Calculate Resistance and Specific Resistance?
Here is describing some important formulas for calculating the value of resistance.
- According to ohm’s law, resistance is directly proportional to the voltage and inversely proportional to an electric current in an electric circuit.
Resistance, (R)= [(Voltage)/(Electric Current)] (Unit- Ohm)
You can calculate the value of resistance by using an online resistance calculator.
[CP_CALCULATED_FIELDS id=”6″]
- The value of resistance is calculated by using a basic formula.
Basically, the resistance of the conductor depends on some important factors such as the length (l) of the conductor, the nature of materials, the cross-section area of the conductor and the temperature of the conductor.
Resistance, (R)= [(Resistivity*Length)/Area]= [(ρ*l)/a] (Unit- Ohm)
And specific resistance or resistivity is calculated from the resistance.
Resistivity, (ρ) = [(Area*Resistance)/Length]= [((a*R)/l)] (Unit- Ohm.meter)
Where, (ρ)- Resistivity or Specific resistance (In geek later is called Rho).
You can calculate the value of specific resistance and resistivity by using the online calculator tool.
[CP_CALCULATED_FIELDS id=”9″]
What is a Resistor?
Definition of Resistor:
The components which provide a specific value of resistance in the electrical circuit is called a ‘Resistor’.
The resistor is a passive component as it can not operate without an energy (voltage) supply or source.
These components of the substance are used to reduce the flowing electric current and control the circuit. It also maintains the voltage level or divides voltage in the circuit, and adjusts the signal level.

Resistor (rating with color code)
If you look at the resistor image, there are 4 color bands pained on it. The colour code of the resistor depends on the resistance rating.
If you want to know the value of the resistor, you can calculate the value of resistance by using colour band. We can use these color bands to calculate the value of the resistor.
You can buy different ratings of resistors as per your requirements.
What are the different types of Resistors?
There are basically two types of the resistor as given below.
1. Fixed types of Resistor:
A fixed type of resistor has a specific value or constant value. We can’t change the value of the fixed resistor.
The carbon film, metal film, metal oxide film, carbon composition, wire wound, etc. are examples of fixed types of resistors.
2. Variable types of Resistor:
The variable type of resistor works as per the name of the resistor. The variable resistor consists of different values which can be changed through a dial, knob, and screw or manually by a proper method.
Potentiometers, Rheostats, Photoresistors, Thermistors, and Trimmers are the best examples of the variable types of resistors.
These variable resistors help to control the voltage level as per the requirement or need.
This is all about resistance with their basic concept, formula, and use of resistors.
Here, you can read more about the comparison of resistance-related.
- Resistance Vs Reactance
- Resistance Vs Reluctance
- Series and Parallel Circuit
- Alternating Vs Direct Current
- Electric Motor Vs Generator
I hope you find this article helpful. If you have any queries, feel free to ask me in the comment section below.
Thanks for Reading!
This is really having a simple explanation to remember all those formulas. Thanks!
You’re welcome, Tom!
And glad to see you here.
You are doing a good job. All the best.
Thanks, Abhishek 🙂
This is a good one, Dipali.
Thanks, Harry 🙂
thankyou so much sis Dipali! felt so left behind but your website made me feel like im back on track!