Hi, readers welcome to the next article continuing our learning journey to in-depth Railway Electrification learning.
In this article, we are going to discuss some basics before understanding more about the Traction Substation.
So, you might be wondering is there any difference between the normal substation and
traction substation?
Yes, there is only one major difference that is in normal substation stepping down of the same phase is done while in TSS 3-phase is stepped done to a single phase.
Read more related- Single-phase vs three-phase AC systems
I am attaching the schematics just for your reference and knowledge.
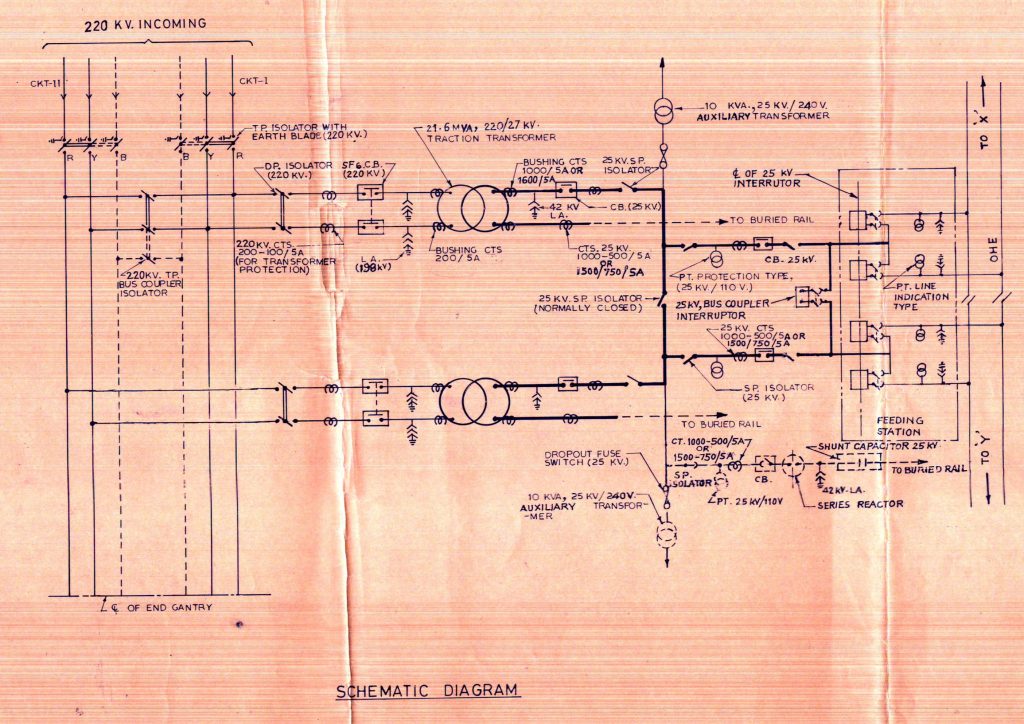
Let’s learn about the components used in the traction substation with an example of a 132/25kV
traction substation.
Components Used in Traction Substation | with an Example
- Power is tapped from the grid and it faces its first safety component that is the Double pole isolator with an earth blade, Isolator is an off-load switch used in the power system to isolate the section along with the coordination with the circuit breaker and discharge it via the earth blade.
- As there is a double-phase transmission feed in the case of two transformer setups, a double pole isolator would be in the center to transfer the power from one circuit to another and feed to the transformer via several protective electrical components.
- Now comes the Lightning Arrestor as the name suggests it surges the lightning without allowing its damage to future components. Note: In some schematics, you might observe the lightning arrestor before the double pole isolator just for safety and in case the length of the transmission line is more than 4km from the grid station of the state electricity board to the traction substation.
- The next component is the current transformer as you all must be aware of its usage of metering the high-rated current value to the lower value, they are also of various types based on class.
- The next component in the schematic you would observe is the circuit breaker depending upon the maximum rated value of full load rated current and short circuit current capacity an engineer needs to make a choice among the MCB, MCCB, ACB, and VCB Generally we used SF6 Circuit Breaker where SF6 being the electronegative gas have the affinity towards ions and resulting in safe quenching of arch while breaking and making operation.
- The most expensive component in the traction substation is the traction transformer so we need to take each and every protection to avoid its failure like Baffle Wall when two transformers are proposed we used to propose a wall in between them. So is 198kV LA You must be wondering how we decide the value of the lightning arrestor we would discuss his in the upcoming article.
- The next component is the traction transformer, In railways as per the research design and standard organization. There are broadly two standards adopted 132/25kV traction substation and 220/27kV traction substation, Considering the requirement it is pointed out in the tender document to the client. The rating of the transformer is mentioned in the tender but as an electrical engineer, you can also calculate the MVA rating of the transformer by the load requirement method, Here we are using a 21.6MVA rating transformer.
Note: We are considering 25kV OHE not 2X25.
While traveling in a train you must have observed substations you must come across the string of conductors hanging from the top ever wondered about what they are called you must be amazed just by knowing their names, have you heard of Zebra, Moose, Tiger, and Bull conductors, Yes, these are the name of ACSR conductors.
In railways considering 220kV side, we use 28.62mm aluminum conductor steel reinforced bull conductor.
I guess this article will give you a brief overview of the traction substation components in
the next article we would learn about the components on the secondary side in detail.