
In an electronics or telecommunication system, signal plays a prominent role in carrying information of fundamental electrical quantities.
Electrical quantities (like the voltage, current, and frequency) varries with respect to the time in the form of an electrical signals.
The standard definition of the signal is a single-valued function of variables that conveys some information of fundamental quantities.
There are mainly two different types of signals used in an electronic system.
- Analog Signal or Continuous Signal
- Digital Signal or Discrete Signal
In this tutorial we will learn the difference between analog and digital signal in detail.
What is the difference between analog and digital signal?
| # | Contents | Analog Signal | Digital Signal |
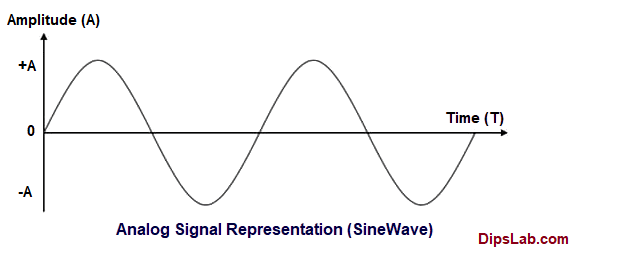
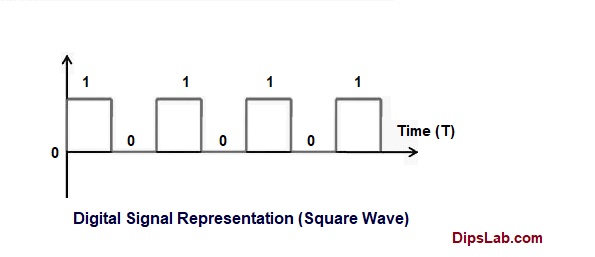
| 01 | Definition | A signal which continuously varies with respect to the time is called ‘Analog Signal’. | A signal which varies only at a certain level with respect to time instant is called ‘Digital Signal’. |
| 02 | Nature | Analog signal occurs in continuous nature. | Digital signal occurs in Discontinuous nature. |
| 03 | Representation | Basically, it is represented by the Sin or Cosine wave. | It is represented by the Square wave. |
| 04 | Carry Information | This signal carries data values in a continuous (not specific) range. | This signal carries data values in a discrete or binary (like zero or one) range. |
| 05 | Data Accuracy | It provides information with high accuracy. | It provides information with low accuracy as compared to the analog signal. |
| 06 | Polarity | Analog signal operates on the positive (+) and negative (-) polarities. | Digital signal operates only on the positive (+) polarities. |
| 07 | Depending Factor | This signal is described by the amplitude, period or frequency, and phase. | This signal is described by the bit rate and bit intervals. |
| 08 | Transmit Data | Analog signal transmits data in the form of waves. | Digital signal transmits data in the form of binary numbers. |
| 09 | Bandwidth | It requires a low bandwidth as compared to the digital signal. | It requires more bandwidth. |
| 10 | Electric Power | For the analog signal, more power is required to transmit data. | For the digital signal, less power is required to transmit data. |
| 11 | Examples | Earphones, Human voices, FM radio signals, photocells, Light sensors, etc. are examples of analog signals. | Switch, Computer, Mobile, DVD, Digital pens, PLC etc. are examples of digital signals. |
| 12 | Memory | This signal is stored in the form of a wave signal. | This signal is stored in the form of a binary bit. |
| 13 | Analysis | Analog signal is very difficult to analyze. | Digital signal is very easy to analyze as compare to the analog signal. |
| 14 | Signal Effect | It conveys the information with high noise and distortion than the digital signal. | It conveys information with less noise and distortion. |
15. Representation of the Analog and Digital Signals:
- Analog Signal or Continuous-Time Signal:
- Digital Signal or Discrete-Time Signal:
This is all about the difference between analog and digital signal.
If you have any queries regarding this comparison, drop your comment below.
Other Related Comparisons:
- Electrical vs Electronics
- Active vs Passive Component
- Electrical vs Magnetic Circuit
- Single vs Three Phase
- Alternating vs Direct Current
- Series vs Parallel Circuit
Thanks for Reading!