Equivalent Current Calculator
[CP_CALCULATED_FIELDS id=”57″]
Equivalent Voltage Calculator
[CP_CALCULATED_FIELDS id=”55″]
Equivalent Series Resistance Calculator
[CP_CALCULATED_FIELDS id=”52″]
Equivalent Parallel Resistance Calculator
[CP_CALCULATED_FIELDS id=”53″]
Equivalent Series Conductance Calculator
[CP_CALCULATED_FIELDS id=”63″]
Equivalent Parallel Conductance Calculator
[CP_CALCULATED_FIELDS id=”64″]
Equivalent Series Capacitance Calculator
[CP_CALCULATED_FIELDS id=”58″]
Equivalent Parallel Capacitance Calculator
[CP_CALCULATED_FIELDS id=”60″]
Equivalent Series Inductance Calculator
[CP_CALCULATED_FIELDS id=”61″]
Equivalent Parallel Inductance Calculator
[CP_CALCULATED_FIELDS id=”62″]
Equivalent Series and Parallel Circuit Calculator
Here, we are studying about the equivalent or total series circuit and parallel circuit connection calculation.
Firstly, you should know about basic concept such as the series and parallel circuit connection with connected different elements.
In an earlier tutorial, I have explained about the Series Circuit and Parallel Circuit with an example.
1. Series Circuit Calculator-
In a series circuit connection, the number of electrical elements or components are connected in series or sequential form.
For example, the given circuit is said to be series circuit, when electronics components (such as resistance R1, R2 and R3) are connected in a single path with connected voltage source (Vs).
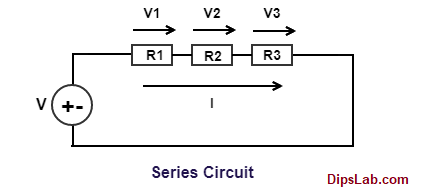
When voltage source is given to a circuit, the same current is flowing (I). But, different (or drop) voltage (V1, V2, and V3) occurred across all the serial connected resistance.
The sum of voltage drops in individual series connected resistances is equal to the applied voltage (i..e V= V1+V2+V3).
Let’s check, here some important formulas for different connected components in series circuit.
Total Current, (Ieq) = (I1= I2 = I3 = I4 = 15 = ......= In) (Unit- Ampere)
For the calculation of voltage in Series:
Total Current, (Veq) = (V1+ V2 + V3 + V4 = V5 = ......= Vn) (Unit- Volt)
Total Resistance, (Req) = (R1+ R2 + R3 + R4 + R5 +......+ Rn) (Unit- Ohm)
Total Conductance, (Geq) = [1 / ((1/G1) + (1/G2) + (1/G3) + (1/G4) + (1/G5) +......+ (1/Gn))] (Unit- Siemens)
Total Capacitance, (Ceq) = [1 / ((1/C1) + (1/C2) + (1/C3) + (1/C4) + (1/C5) +......+ (1/Cn))] (Unit- Farad)
Total Inductance, (Leq) = (L1 + L2 + L3 + L4 + L5......+ Ln) (Unit- Henry)
This is the simple description about the series circuit with the different formulas.
2. Parallel Circuit Calculator:
In the parallel circuit connection, the number of electrical elements or components are connected in parallel form.
For example, when electronics components (such as resistance R1, R2 and R3) are connected in a parallel branch with connected voltage source (Vs).
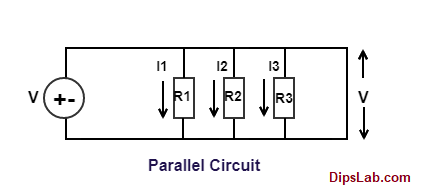
When voltage source is given to a circuit, the same current is flowing (I). But, different (or drop) voltage (V1, V2, and V3) occurred across all the parallel connected resistance.
The sum of voltage drops in individual parallel connected resistances is equal to the applied voltage (i..e V= V1+V2+V3).
Let’s check, here some important formulas for different connected components in parallel circuit.
Total Current, (Ieq) = (I1 + I2 + I3 + I4 + 15 + ......+ In) (Unit- Ampere)
Total Voltage, (Veq) = (V1 = V2 = V3 = V4 = V5 =......+ Vn) (Unit- Volt)
For the calculation of Resistance in Parallel:
Total Resistance, (Req) = [1/((1/R1) + (1/R2) + (1/R3) + (1/R4) + (1/R5) +......+ (1/Rn))] (Unit- Ohm)
For the calculation of Conductance in Series:
Total Conductance, (Geq) = (G1 + G2 + G3 + G4 + G5 +......+ Gn) (Unit- Siemens)
For the calculation of Capacitance in Series:
Total Capacitance, (Ceq) = (C1 + C2 + C3 + C4 + C5 +......+ Cn) (Unit- Farad)
Total Inductance, (Leq) = [1 / ((1/L1) + (1/L2) + (1/L3) + (1/L4) + (1/L5) +......+ (1/Ln))] (Unit- Henry)